The impact of the extent of mortar filling of brick holes on thermal conductivity of masonry
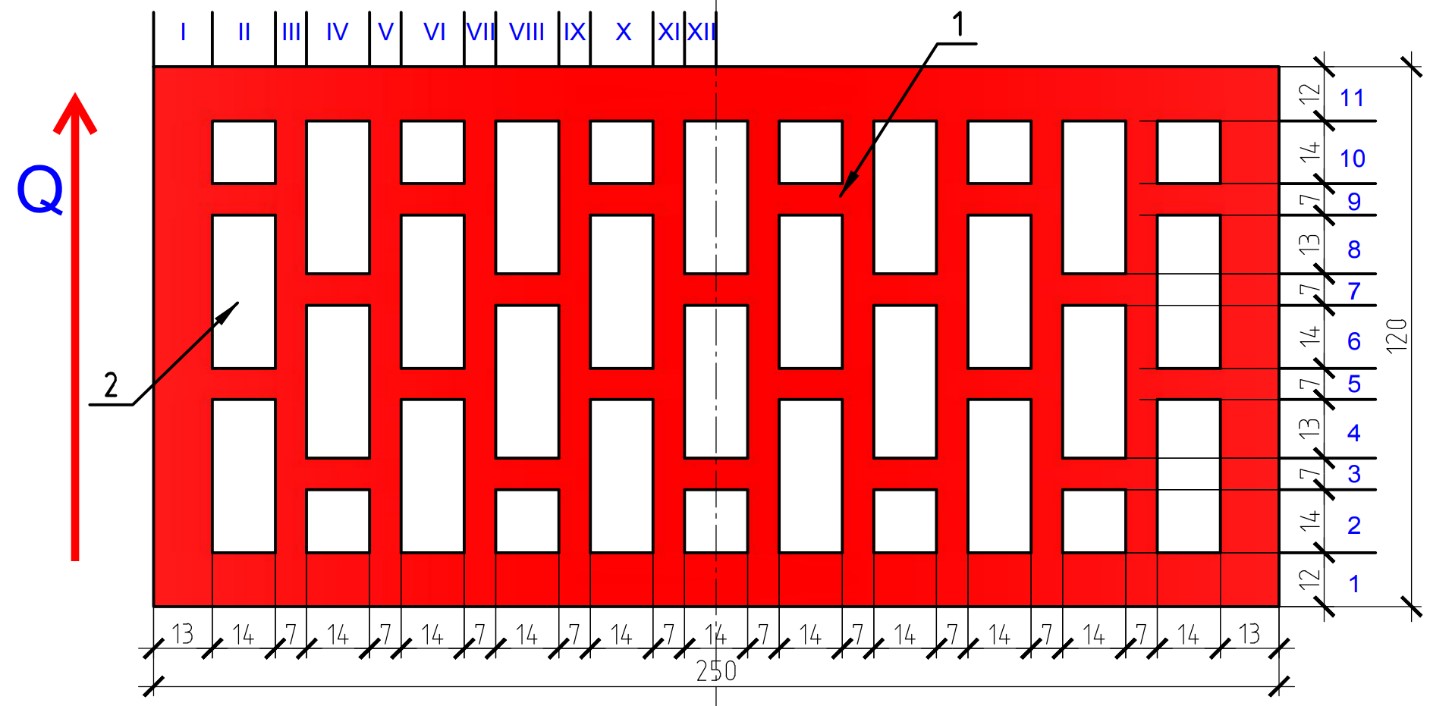
The paper presents a method of calculation the thermal conductivity of perforated ceramic bricks and masonry made of them. The authors calculate the thermal resistance and average thermal conductivity of the facing stone layer with a thickness of 120 mm. Filling holes with mortar leads to an increase in the thermal conductivity of ceramic products and deterioration of their thermal insulation characteristics. The average values of thermal conductivity of face ceramics products and the masonry at different extents of filling of the holes of the mortar are obtained. In case of full filling the holes the thermal conductivity of masonry from perforated bricks becomes comparable with the thermal conductivity of masonry from bricks. In view of this operational thermal conductivity of masonry from perforated facing bricks is higher than the declared value. This fact should be taken into consideration for designing of the facing stone layer from ceramic perforated brick.
.png)


